指南
函数调用
将 xAI 模型连接到外部工具和系统,以构建 AI 助手和各种集成。
介绍
函数调用使语言模型能够使用外部工具,这些工具可以将模型与数字世界和物理世界紧密连接。
这是一项强大的功能,可用于支持广泛的使用案例。
- 调用公共 API 以执行从查找足球比赛结果到获取实时卫星定位数据的各种作
- 分析内部数据库
- 浏览网页
- 执行代码
- 与物理世界互动(例如预订机票、打开特斯拉车门、控制机械臂)
演练
下图演示了函数调用的请求/响应流程。
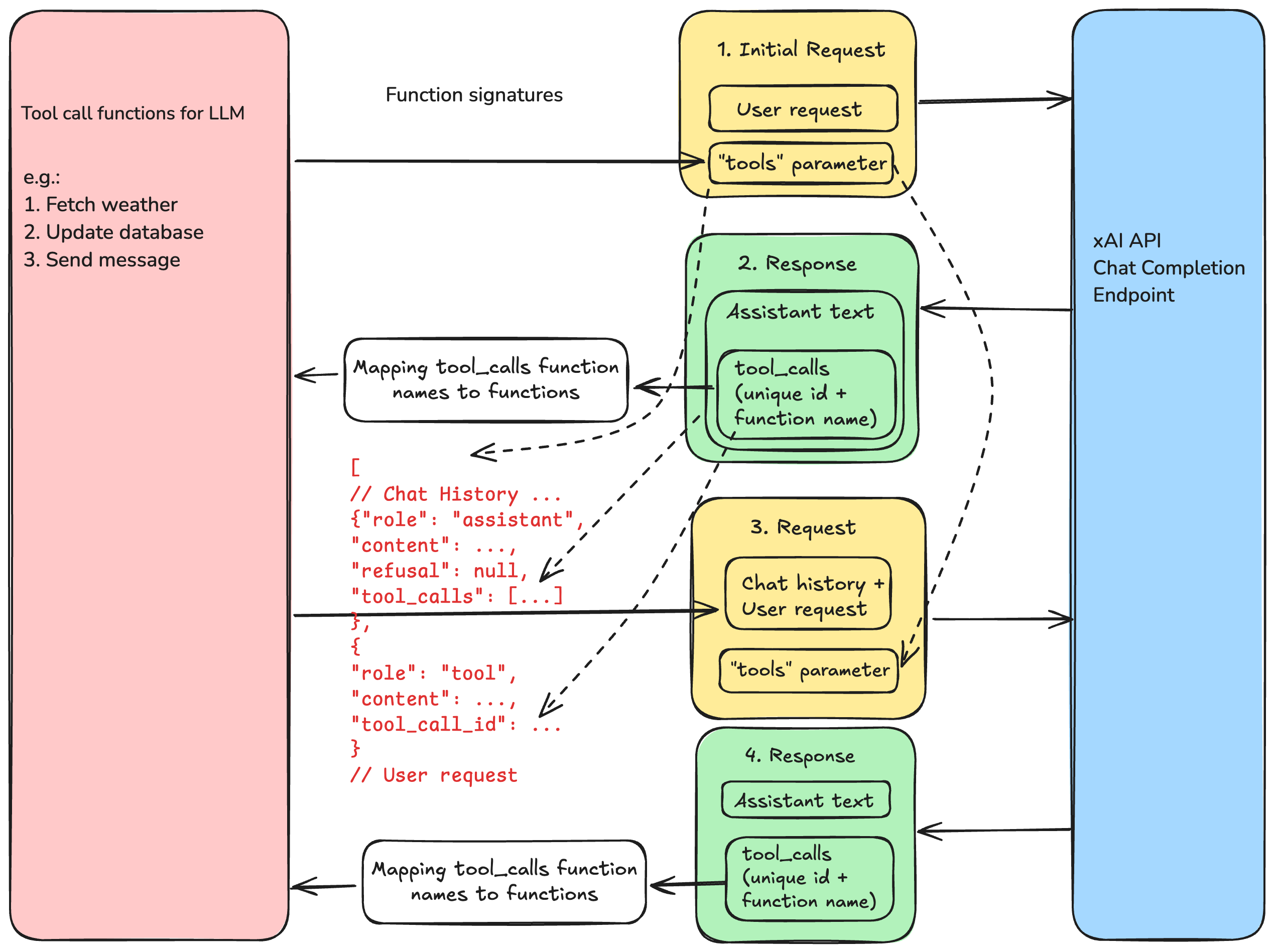
您可以将其视为向用户系统启动 RPC(远程过程调用)的 LLM。从 LLM 的角度来看,“2.Response“ 是从 LLM 到用户系统的 RPC 请求,”3.Request“ 是包含 LLM 所需信息的 RPC 响应。
整个过程在伪代码中如下所示:
伪代码
// ... Define tool calls and their names
messages = []
/* Step 1: Send a new user request */
messages += {<new user request message>}
response = send_request_to_grok(message)
messages += response.choices[0].message // Append assistant response
while (true) {
/* Step 2: Run tool call and add tool call result to messages */
if (response contains tool_call) {
// Grok asks for tool call
for (tool in tool_calls) {
tool_call_result = tool(arguments provided in response) // Perform tool call
messages += tool_call_result // Add result to message
}
}
read(user_request)
if (user_request) {
messages += {<new user request message>}
}
/* Step 3: Send request with tool call result to Grok*/
response = send_request_to_grok(message)
print(response)
}
我们将在以下 Python 脚本中演示函数调用。首先,让我们创建一个 API 客户端:
python
import os
import json
from openai import OpenAI
XAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("XAI_API_KEY")
client = OpenAI(
api_key=XAI_API_KEY,
base_url="https://api.x.ai/v1",
)
准备 - 定义工具功能和功能映射
将工具函数定义为回调函数,以便在模型响应时调用它们。
通常,这些函数会从数据库中检索数据,或调用另一个 API 终端节点,或执行某些作。 出于演示目的,我们硬编码返回 59° Fahrenheit/15° Celus 作为温度,返回 15000 英尺作为云顶。
参数定义将在初始请求中发送到 Grok,因此 Grok 知道哪些工具和参数可以调用。
为了减少人为错误,您可以使用 Pydantic 部分定义工具。
使用 Pydantic 的函数定义:
python
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import Literal
# Defining functions and function arguments
class TemperatureRequest(BaseModel):
location: str = Field(description="The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA")
unit: Literal["celsius", "fahrenheit"] = Field(
"celsius", description="Temperature unit"
)
class CeilingRequest(BaseModel):
location: str = Field(description="The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA")
def get_current_temperature(**kwargs):
request = TemperatureRequest(**kwargs)
temperature: int
if request.unit.lower() == "fahrenheit":
temperature = 59
elif request.unit.lower() == "celsius":
temperature = 15
else:
raise ValueError("unit must be one of fahrenheit or celsius")
return {
"location": request.location,
"temperature": temperature,
"unit": "fahrenheit",
}
def get_current_ceiling(**kwargs):
request = CeilingRequest(**kwargs)
return {
"location": request.location,
"ceiling": 15000,
"ceiling_type": "broken",
"unit": "ft",
}
# Generate the JSON schema
get_current_temperature_schema = TemperatureRequest.model_json_schema()
get_current_ceiling_schema = CeilingRequest.model_json_schema()
# Definition of parameters with Pydantic JSON schema
tools_definition = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Get the current temperature in a given location",
"parameters": get_current_temperature_schema,
},
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_ceiling",
"description": "Get the current cloud ceiling in a given location",
"parameters": get_current_ceiling_schema,
},
},
]
使用原始字典的函数定义:
python
# Defining functions
def get_current_temperature(location: str, unit: str = "fahrenheit"):
temperature: int
if unit.lower() == "fahrenheit":
temperature = 59
elif unit.lower() == "celsius":
temperature = 15
else:
raise ValueError("unit must be one of fahrenheit or celsius")
return {"location": location, "temperature": temperature, "unit": "fahrenheit"}
def get_current_ceiling(location: str):
return {
"location": location,
"ceiling": 15000,
"ceiling_type": "broken",
"unit": "ft",
}
tools_map = {
"get_current_temperature": get_current_temperature,
"get_current_ceiling": get_current_ceiling,
}
# Raw dictionary definition of parameters
tools_definition = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Get the current temperature in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"default": "celsius"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_ceiling",
"description": "Get the current cloud ceiling in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}
]
创建一个 string -> 函数映射,这样我们就可以在模型发送函数名称时调用该函数。例如
python
tools_map = {
"get_current_temperature": get_current_temperature,
"get_current_ceiling": get_current_ceiling,
}
1. 发送初始消息
定义完所有函数后,是时候将我们的 API 请求发送到 Grok 了!
现在,在我们发送之前,让我们看看新任务的通用请求正文是什么样子的。
请注意 tool 调用是如何被引用三次的:
- 由
id和name在 “上一次 Assistant 响应以获取工具调用” 中 - 由
tool_call_id在 “Tool Call return” 中 - 在
tools请求正文的字段
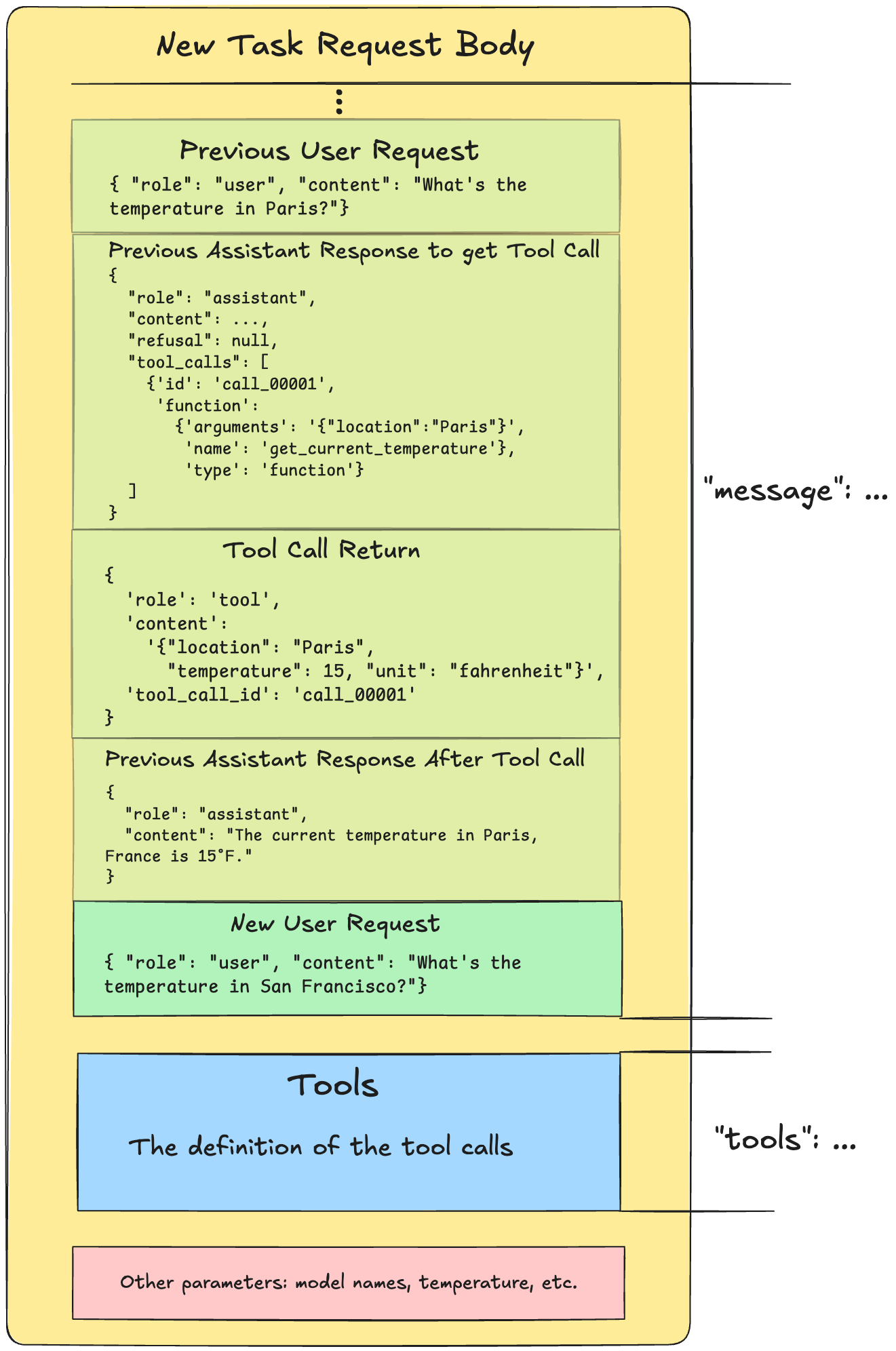
现在,我们在请求正文中编写请求消息并将其发送到 Grok。Grok 应该返回一个响应,要求我们进行工具调用。
python
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the temperature like in Paris?"}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="grok-2-latest",
messages=messages,
tools=tools_definition, # The dictionary of our functions and their parameters
tool_choice="auto",
)
# You can inspect the response which contains a tool call
print(response.choices[0].message)
2. 如果 Grok 要求工具调用并将函数返回到消息,则运行工具函数
我们检索 Grok 想要调用的工具函数名称和参数,运行函数,并将结果添加到消息中。
此时,您可以选择仅使用结果响应工具调用或添加新的用户消息请求。
这toolmessage 将包含以下内容:{ "role": "tool", "content": <json string of tool function's returned object>, "tool_call_id": <tool_call.id included in the tool call response by Grok>}
我们尝试组装并发送回 Grok 的请求正文。请注意,它看起来与新的任务请求正文略有不同:
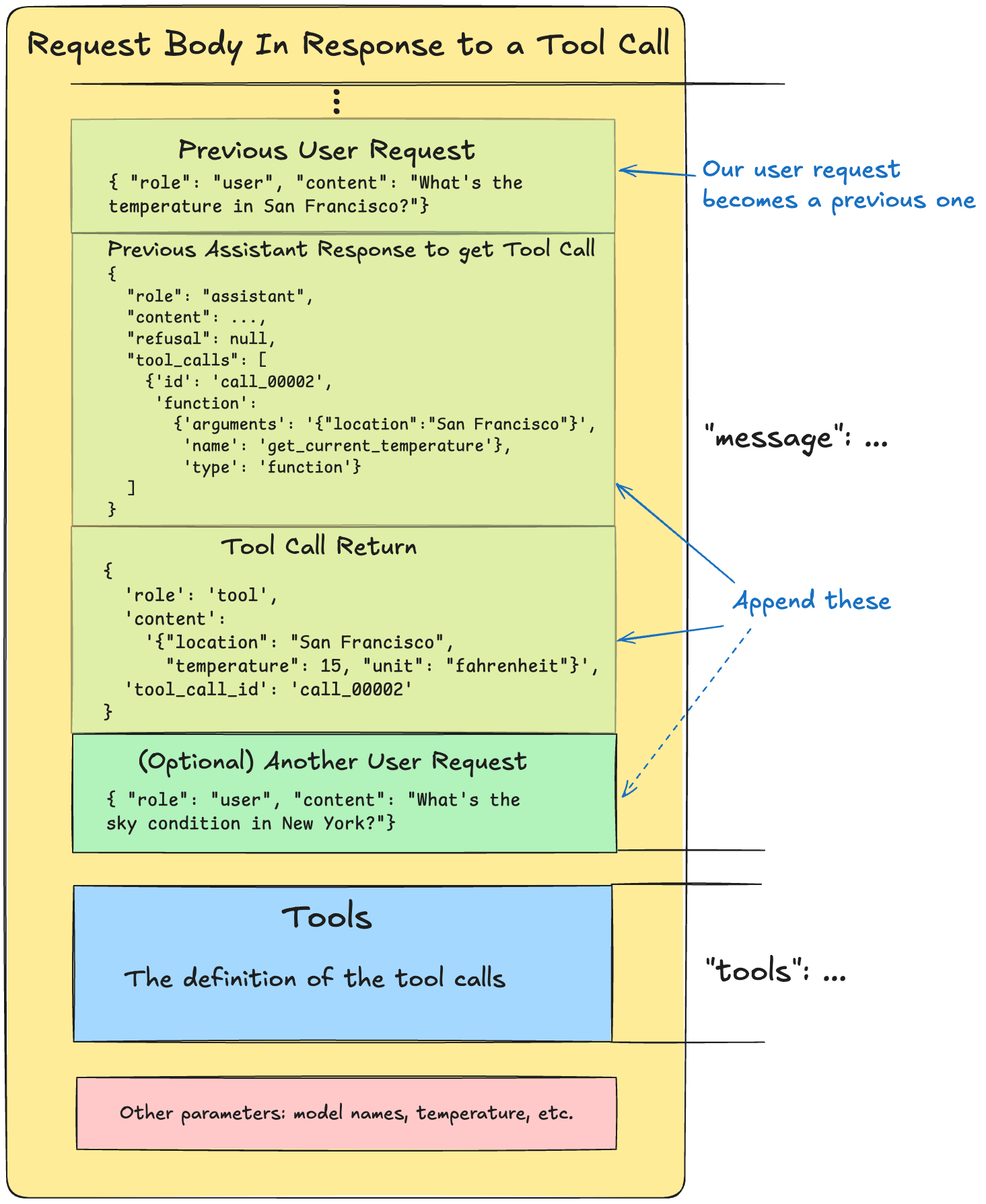
用于附加消息的相应代码:
python
# Append assistant message including tool calls to messages
messages.append(response.choices[0].message)
# Check if there is any tool calls in response body
# You can also wrap this in a function to make the code cleaner
if response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
for tool_call in response.choices[0].message.tool_calls:
# Get the tool function name and arguments Grok wants to call
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_args = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# Call one of the tool function defined earlier with arguments
result = tools_map[function_name](**function_args)
# Append the result from tool function call to the chat message history,
# with "role": "tool"
messages.append(
{
"role": "tool",
"content": json.dumps(result),
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id # tool_call.id supplied in Grok's response
}
)
3. 将 tool 函数返回发送回模型以获取响应
python
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="grok-2-latest",
messages=messages,
tools=tools_definition,
tool_choice="auto"
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
4. (可选)继续对话
您可以按照步骤 2 继续对话。否则,您可以终止。
函数调用模式
默认情况下,模型将自动决定是否需要调用函数,并选择要调用的函数,由tool_choice: "auto"设置。
我们提供三种方法来自定义默认行为:
- 要强制模型始终调用一个或多个函数,您可以设置
tool_choice: "required".然后,模型将始终调用 function。请注意,这可能会强制模型产生幻觉参数。 - 要强制模型调用特定函数,您可以设置
tool_choice: {"type": "function", "function": {"name": "my_function"}}. - 要禁用函数调用并强制模型仅生成面向用户的消息,您可以不提供任何工具,或者将
tool_choice: "none".